Introduction to Engineered Stone for Beginners
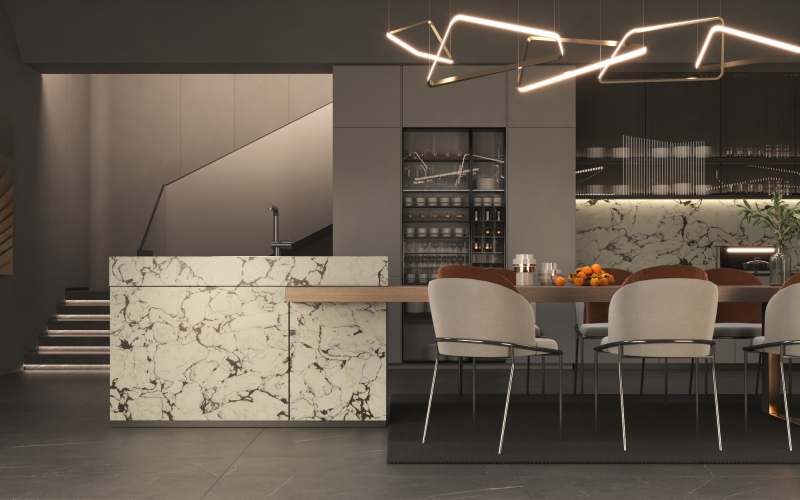

When selecting a countertop material, engineered stone stands out as a top contender for several
compelling reasons. It is eco-friendly, requires minimal maintenance, and serves as a great alternative
to natural stone. Although engineered stone has advanced significantly, not everyone is familiar with
its features.
If you're interested in discovering more about engineered stone, you're in the right place. In this guide,
we'll explore the various aspects of engineered stone, including its advantages and disadvantages,
different types, and why it might be the ideal choice for your home's surfaces.
What Is Engineered Stone?
Engineered stone, often considered an alternative to natural stone, combines both natural and synthetic
elements. Designed to address some of the limitations of natural stone, engineered stone offers
affordability, durability, and a range of aesthetic options. It typically features uniform colors, consistent
thickness, and various hue variations that are not always present in natural stone.
Generally composed of 90 to 95% crushed quartz mixed with polymer resin, engineered stone may also
include other materials like shells, mirrors, and metals. Recently, a new variant has emerged, consisting
of 30% vinyl and 70% ceramic.
Engineered stone is used in similar applications to natural stone, including bathroom and kitchen
surfaces. It is particularly popular for backsplashes, flooring, countertops, and benchtops due to its
versatility and practical benefits.
Pros of Engineered Stone
Here are some notable advantages of engineered stone:
1. Durability
Engineered stone benefits from the high durability of quartz, which constitutes the majority of its
composition. Combined with advanced resin technology, this makes engineered stone exceptionally
tough, capable of withstanding heat, scratches, and cracks. Its robustness makes it suitable for a variety
of surfaces, ensuring long-term performance.
2. Resistance
Engineered stone surpasses natural stone in resistance to scratches, stains, and heat. This makes it an
ideal choice for kitchens, where exposure to hot pots, spills, and other potential hazards is common.
You can confidently place hot cookware or accidentally spill acidic substances without worrying about
damage.
3. Variety of Options
Engineered stone offers a wide array of colors, patterns, and designs, allowing it to seamlessly
integrate with various interior styles. Whether you prefer the look of marble or granite, engineered
stone can replicate these natural patterns, providing the aesthetic appeal of real stone with added
benefits.
4. Low Maintenance
Engineered stone surfaces are easy to maintain. Unlike traditional materials such as marble or granite,
they do not require frequent resealing to preserve their appearance. Regular cleaning with standard
household products is typically sufficient to keep them looking new.
5. Affordability
Generally more cost-effective than natural stone, engineered stone offers significant value. With lower
ongoing maintenance costs and often comes with a substantial warranty, it represents a smart
investment for both budget-conscious and quality-seeking homeowners.
Cons of Engineered Stone
While engineered stone offers many benefits, it also has some drawbacks. These disadvantages can vary
based on personal preferences and specific needs:
1. Lack of Natural Variation
If you appreciate the unique imperfections and irregularities of natural stone, engineered stone might
not be the ideal choice. Engineered stone is designed to provide a consistent appearance with uniform
colors and patterns, which might lack the distinctive character found in natural stone.
2. Heat Sensitivity
Although engineered stone is more heat-resistant than many materials, it is not entirely immune to
heat damage. Since it contains resin—a type of plastic—exposure to high temperatures can potentially
cause discoloration or other issues. It’s important to use trivets or hot pads to protect the surface from
extreme heat.